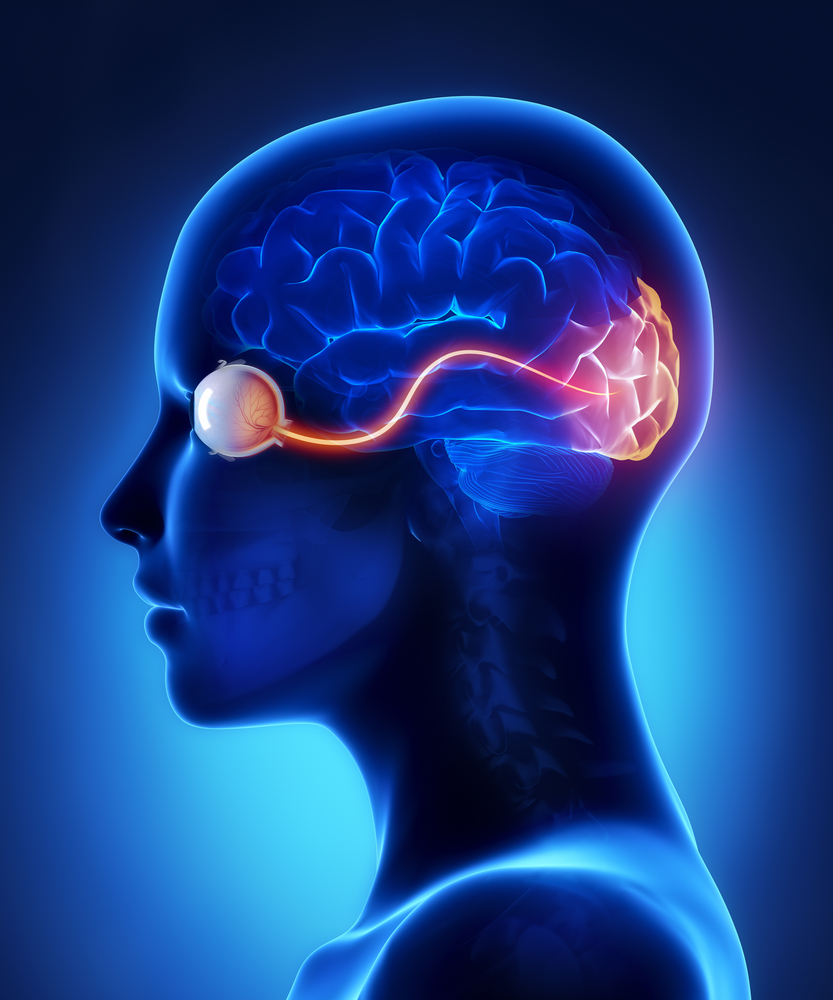
optic nerve connects to what part of the brain
The optic nerve, a cable–like grouping of nervus fibers, connects and transmits visual data from the eye to the brain. The optic nerve is mainly composed of retinal ganglion prison cell (RGC) axons. In the man middle, the optic nerve receives lite signals from well-nigh 125 meg photoreceptor cells (known as rods and cones) via two intermediate neuron types, bipolar and amacrine cells. In the brain, the optic nervus transmits vision signals to the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), where visual information is relayed to the visual cortex of the brain that converts the epitome impulses into objects that we see.
In the retinal tissues of the eye, more than 23 types of RGCs vary significantly in terms of their morphology, connections, and responses to visual stimulation. Those visual transmitting RGCs are the neuronal cells. They all share the defining properties of:
Human beings tin can encounter three main colors: red, dark-green, and blueish. This is due to our having three dissimilar kinds of colour sensitive cone cells: red cones, green cones, and bluish cones. The RGCs connecting to the red and green cones are midget RGCs. They are mainly located at the center of the retina (known as fovea). A single midget RGC communicates with equally few as five photoreceptors. They transmit cherry-red-green color signals to the parvocellular layer in the LGN (see Effigy). The midget-parvocellular pathway responds to color changes, but has piddling or no response to contrast change. This pathway has center-surround receptive fields, and ho-hum conduction velocities. Considering of this pathway, nosotros tin see objects precisely in detail and in full color. Objects can be seen in the dark with move and fibroid outlines accentuated due to the parasol RGCs. At the periphery of the retina, a single parasol RGC connects to many thousands of photoreceptors (many rods and few cones). The parasol RGCs project their axons to the magnocellular layers of the LGN (run across Effigy) and are primarily concerned with visual perception. They take fast conduction velocities, can respond to low-contrast stimuli, just are not very sensitive to changes in color. Finally, humans tin can see objects in three-dimension courtesy of the crossing over of optic nerve fibers at the optic chiasm. This anatomic structure allows for the man visual cortex to receive the aforementioned hemispheric visual field from both optics (see Figure), thus making it possible for the visual cortex to generate binocular and stereoscopic vision. Recently, a new type of RGC, called photosensitive RGCs, was discovered. The photosensitive RGCs contribute minimally to our vision, but play a key function in vision regulation. Photosensitive RGCs axons practise not accept connections to the LGN, simply form the retino-hypothalamic tract, and synapse to iii other locations in the brain for specific vision regulation functions: A fully functional optic nerve is essential for vision. Evidently, whatsoever damage of the optic nerve will sever the precise transmission of visual information between the retina and brain, directly leading to vision distortion and/or vision loss. Damage to the optic nerve can issue from: Moreover, the optic nerve is also a very important vivo model for studying central nervous protection and regeneration. At the cell biology level, the RGC axons are covered with myelin produced past oligodendrocytes (rather than Schwann cells of the peripheral nervous organisation) subsequently exiting the eye on their way to the LGN and thus function of the primal nervous system. Scientists take recently acquired more than and more than evidence that sure types of damage to the optic nerve may be reversible in the futurity. Therefore, the optic nervus provides a potential window to explore more complicated neuronal degenerative diseases, such equally Alzheimer's disease and Huntington disease. three/12/15
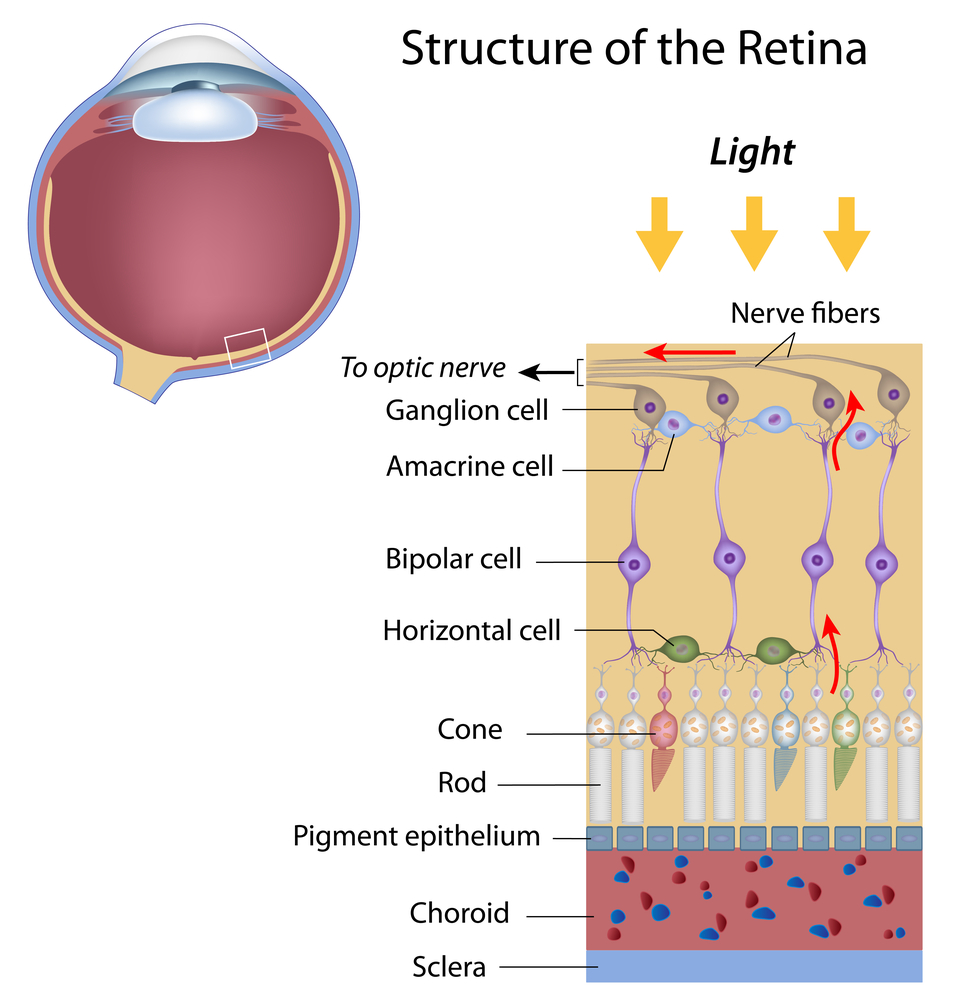
The bistratified RGCs are likely involved in blue color vision. Bistratified cells receive visual information input originally from an intermediate numbers of cones and rods. The bistratified RGCs connect to the koniocellular layers in the LGN (see Figure). The koniocellular neurons grade robust layers throughout the visual hemifield and have moderate spatial resolution, moderate conduction velocities, and can respond to moderate-contrast stimuli. They accept very large receptive fields that just possess on-center regions (no off-surround regions).
 Jun Lin, MD, PhD
Jun Lin, MD, PhD
Assistant Professor,
Department of Ophthalmology
New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai
Icahn Schoolhouse of Medicine at Mount Sinai
—–
 James Tsai, Dr., MBA
James Tsai, Dr., MBA
Chair, National Eye Health Education Program Glaucoma
Subcommittee President, New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mountain Sinai Chair
Section of Ophthalmology
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Source: https://discoveryeye.org/optic-nerve-visual-link-brain/
0 Response to "optic nerve connects to what part of the brain"
Postar um comentário